Seoul Metropolitan Subway Coporation
|
Changes in traffic conditions and the subway |
With the foundation of the Chosun Kingdom, Seoul became the capital of the Korean peninsula. Since then, for 600 years Seoul has been the center of Korean history. It is also an international metropolis, symbolizing today's Korea as it shifts from a highly industrial society to an information-centered society. After the 1960s, due to the high economic development, abrupt expansion occurred again and again. Industry and population concentrated in Seoul, and downtown development reached its limit. As a result, in the 1970s new commercial and business sections were built on the outskirts, and the residential areas spread out quickly to the suburbs and throughout the capital region. To this tendency, smooth connection between diverse principal regions became important, but due to the shortage of road space and a rapid increase of cars, the existing road network in Seoul could no longer handle the exploding traffic demand. A fast and large-scale subway transport arose as the only alternative plan to solve the traffic congestion. |
|
Establishment and development of the subway system |
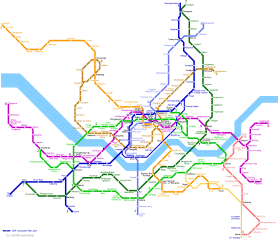
Seoul decided to build the subway to expand the lacking transportation, and inaugurated a subway construction headquarters on June 8, 1970. The next year on April 12 construction started on the Seoul subway number 1 line. Three years and four months after the inauguration of the Subway Corporation, on August 15, 1974, we had a historical formal opening of the 7.8km long section linking Seoul Station and Chongnyangni. Hence Seoul lifted the curtain of its subway era as the 22nd country and 49th city in the world to have a subway. In February 1980, which line 2 was under construction, 23 private enterprises established together the Seoul Subway Construction Co. Ltd., to construct lines 3 and 4. They broke up. however, due to lack of efficiency. Then on September 1, 1981, the Seoul Metropolitan Subway Corporation (SMSC), Korea's first public local corporation, was established and took charge of construction and operation of the subway. The Seoul Metropolitan Subway Corporation was established to promote public welfare by providing safe and rapid traffic service. With capital of 50 billion won. Later, it embarked upon the efficient construction of lines 3 and 4. The company was at that time operating lines 1 and 2. After the opening of Line 1 in 1974 the Seoul subway made partial opening in five steps. At last on May 22, 1984, line 2, the circulation route had its complete opening, linking the areas south and north of the Han river in a ring shape. The opening of Line 2 helped solve Seoul's traffic problems by linking downtown, the suburbs, and newly commercial residential all in one ring. Lines 3 and 4, crossing downtown diagonally, began construction in February 1980 and opened on October 18, 1985. The Seoul subway was thus able to link southern and northern parts of Seoul with the downtown as well as with the Seoul outskirts. Later, in the 1990s, the SMSC repeated these development by opening branches of line 2 and extensions of Lines 3 and 4. The growth of the SMSC is most easily confirmed through external measurements such as the numeric increase of electric railcars and their capacity, or by the number of passengers. The subway Corporation had 60 electric railcars at the opening for Line 1 but after 10 years, in 1984 when Line 2 opened, the number had increased to 344, six times more. After another 10 years, in 1994, when the branches of Line 2 and the extensions of lines 3 and 4 were finished, the number increased to 1,872. Now as of the end of 1995 the SMSC has 1,944 railcars. This means that the number of railcars has multiplied by 32 times over 20 years, and it shows clearly the growth of the SMSC. The extension of operation has also developed quite well from the viewpoint of international comparison. The Seoul Subway started with 7.8 km and extended to 62km when line 2 opened. At the end of 1995 it had 134.9 km of operational trackage, which compares favorably with the systems in other developed countries. Due to a continuous qualitative development such as operational extension, passengers using the subway have increased greatly in the past 20 years. In the first year passenger trips amounted to about 30 million but in 1977 the number exceeded 100 million. Then in 1995, eleven years after the opening, it passed the 500 million mark, and trips on Line 2 outnumbered those on Line 1. The number of passengers began to exceed one billion per year starting from 1989. Seoul Subway finds its total passenger trips in 1995 at 1.4 billion. On average people use the subway more than 4 million times every day. This figure is the 4th highest in the world, and also shows the relative importance of the subway among other means of public transportation in Seoul. As well as these external developments, the Seoul subway is making efforts in the field of safety and service. Providing a unique culture through rapid, comfortable and safe transportation, it is emerging as the principal means of getting around in Seoul. |
|
|
|
|

|
Seoul Subway ticket bought at Hyehwa station on a sunny day in August 2000. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
S u b w a
yAA
d v e r t i s i n gAi
nAT
a i p e i - S e o u l - B e i j i n
g